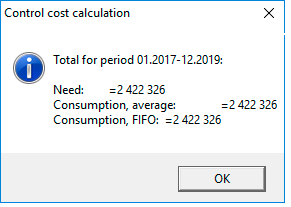Procurement plan and regulatory costs. Practical planning
Algorithm for planning purchases and standard costs
For the fastest and most reliable planning of purchase prices, the program has powerful tools - for planning and adjusting prices of any complexity, including in the face of changing external factors.
 Budget-Plan Express is a software product for preparing business plans and presentations in Word and Excel format, optimal for small businesses and studies (for students, graduate students, MBI students, etc.)
Budget-Plan Express is a software product for preparing business plans and presentations in Word and Excel format, optimal for small businesses and studies (for students, graduate students, MBI students, etc.)
Build a financial model of your project or calculate loan financing on different terms! Try the new version of the program (6.02). Details ...

Procurement and regulatory cost planning is the planning of price and consumption within 36 months (standard planning horizon) of regulatory and other direct costs, taking into account taxes, procurement schedule, inventory and taking into account the influence of external factors.
☛ Important! An additional conditional future period has been added to all plans. However, only in the plans of loan and rental products can you plan with an estimated horizon of up to 10 years (up to 120 months). At the same time, all calculations - outside the standard horizon - will be taken into account in the conditional future period. That is, the future period will accumulate all the calculations that will go beyond the 36 months of the project.
☛ The purchase plan and standard costs are directly related to the sales plan, since the consumption (standard) of the costs per unit of the product from the sales plan is indicated here. In other words, in this plan we do not indicate the quantity (volume of purchases), instead, we indicate the expense. And therefore, the volume of purchases is calculated here automatically - taking into account the sales plan, safety stocks (sales and purchases) and the purchase schedule.
If the company is engaged in, for example, wholesales, purchases are also in fact standard costs with an expense ratio equal to one.
☛ Please note that the purchase schedule and safety stock are only specified when the costs are of material type. That is, the reference book must indicate the type of material costs (materials and components).
General planning algorithm
First, in the "Table of purchases and standard costs" tab, the purchase price is planned. Then, in the "Consumption (standard)" tab, a product is selected and the consumption per unit of product is indicated. Consumption can be specified for one or several products.
If this type of cost is material (materials, components), you can additionally detail the procurement schedule (the "Purchase schedule" tab) and specify the monthly safety stock (the "Material inventory accounting" tab). Tax (VAT) is calculated automatically, the one that is specified in the settings.
Scheduling algorithm - step by atep
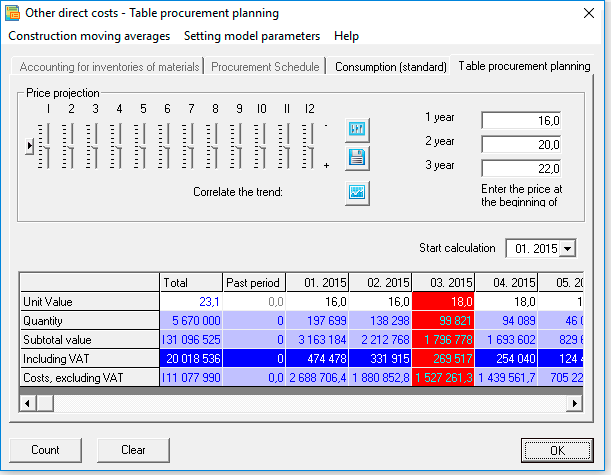
Step 1. Price planning. Procurement and regulatory cost table tab
Price planning algorithm 1. If you have static (not changing, rarely changing) prices
In this case, just enter the price values using normal editing, or enter the value in the initial period, then right-click (above the value field) and select “continue trend” from the menu, and the current value will be set - to the end of the series. You can change the value of the series in any period and perform the function “continue the trend” starting from this period.
Algorithm for price planning 2. Planning, adjusted for seasonal fluctuations (interpolation of the forecast series)
1. First, as in Algorithm 1, the initial field in the price series is filled in, then the series is filled in (the function "continue the trend"). Please note that the "continue trend" function can be used starting from any new period (for example, a year).
2. Next, edit the forecast price trend using the sliders. Values from -100 to +100 are available for the price, i.e., relative price changes (%) from the initial (beginning of the year). To see the values of the slider - move the mouse to the slider. Use the arrows (for the active slider) to set the exact value.
3. Finally, do the price calculation. Click the "Calculate" button, select item 2 in the form: "Adjust the 'Price' series using interpolation of the forecast series." Click OK.
Thus, you will fill in the price series and adjust the series values using forecast series interpolation.
Algorithm for price planning 3 (recommended). Planning by annual values, adjusted for the forecast dynamics of price changes
This is perhaps the most correct way of price planning, since marketing forecasts, when assessing prices, markets, external risks (currencies, etc.), are almost always calculated and guided, at least for the next year.
1. So, first put the price in the field for each year. Then, similarly, use the sliders to adjust the forecast trend “Forecast of the annual price change”.
2. Press the "Calculate" button, in the form select item 1: "Calculate the 'Price' series using annual values and the forecast series". Click OK.
In this case, annual values and forecast series were used.
Step 2. Further price adjustments
In order to most accurately adjust prices, taking into account external and other factors, the program has powerful tools to support complex calculation methods. Moving average models are used for such calculations. For detailed information on these methods, see the Help topics "Adjusting Price Series Using Moving Average" and "Moving Average Model". Also (recommended) watch a video with a detailed explanation of the calculations using these methods (see Lesson 5. Parts 1, 2).
Step 3. Specify the flow rate (standard)
In the next tab "consumption" in the list you need to select a product and in the field "consumption per unit" set the consumption. Note, consumption can be set for one or more products. In front of the products for which consumption has been set, you will see an additional arrow sign on the left side. At the bottom, in the summary line, you will see the total material consumption.
For example, direct electricity costs can be specified for several products and with different target costs for a specific product.
☛ If you have a unique calculation of consumption, for example, defined not in units, but in thousandths, you can specify a special format in the general settings - up to 4 decimal places. Another way (recommended) is to convert the calculations into a single format, for example, grams - into kilograms, kilograms - into tons, etc.
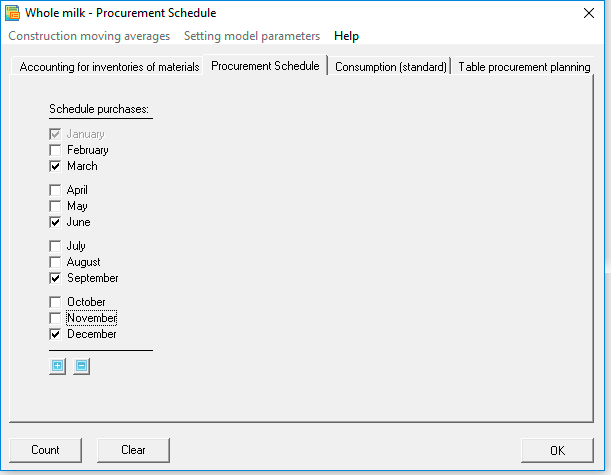
Step 4. If necessary, adjust the procurement schedule
The procurement schedule presents a list of 12 months from January to December. By default, the checkboxes are selected next to each month, which means that the program will "purchase" materials based on the needs of the sales plan. In the same case, if you want to adjust or optimize purchases, for example, taking into account seasonal factors, then you must check the boxes in the months in which the purchases will be made. And in this case, the program will calculate purchases based on the needs of future periods and taking into account safety stocks (sales and purchases).
Step 5. Accounting for safety stock
If necessary, you can take into account the safety stock limit as a percentage. It must be specified as a percentage in the "material inventory accounting" tab. The data in the table "balances of materials and components at the beginning of the period" will appear only after the final calculation.
Step 6. Calculation of the procurement table and standard costs for this cost item (material)
So, all the calculations of the procurement plan and standard costs for this cost item are still in the edit form. When you are convinced that these calculations are final, you can perform the following calculation, after which your calculation will appear in the final table of purchases and standard costs, along with other costs. Click the Read button and select Calculate Purchasing Table and Standard Costs (for this product). Click OK.
Step 7. The final calculation of the procurement plan and standard costs
After all cost plans are ready, you need to do the final calculation. After this calculation, the procurement plan and target costs will be included in the structure of the final calculations of the business plan. Select in the tab of the main menu "data" the menu item "calculate" or press F9. In the form that opens, select the appropriate plan, in this case, the procurement plan (Data → Calculate → Procurement plan. Same thing - F9).
And after the calculation, in addition, taxes (VAT, if it is taken into account), safety stock and other parameters will be calculated, which will be used in the future when calculating the business plan. Now you can go to the edit form, and you will see the calculated tax (VAT, if taken into account) and the safety stock.
Setting of seasonality
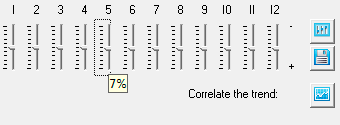
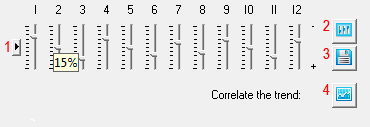
To adjust the values of seasonality, use a special tool - the slider. The acceptable values when planning prices - from "-100" to "+100". Sliders edit seasonal values in percent during the annual cycle (12 months).
The values of the slider can be set with the mouse or arrow keys. First, activate the slider by clicking on it with the mouse, then move the mouse cursor over the slider so that a tooltip appears, as shown in the picture.
Button assignment
- Set default values.
All periods of seasonality are set to "0".
☛ Note that prices are calculated as deviations from a given value, that is, from the seasonality trend.
- Download the trend from the settings of other products.
 When you click a button, a list of costs is offered - select the desired list item. In this case, the corresponding seasonal trend is loaded.
When you click a button, a list of costs is offered - select the desired list item. In this case, the corresponding seasonal trend is loaded.
- Save values.
 When the button is pressed, the current seasonality settings are saved, unsaved seasonal settings will be lost when their form is exited.
When the button is pressed, the current seasonality settings are saved, unsaved seasonal settings will be lost when their form is exited.
- Correlation trend.
 When the button is clicked, a list of trends influencing the pricing is proposed to adjust a number of prices, after which the values of a number of prices will be corrected. The method for adjusting price fluctuations is described in the following paragraphs of this section.
When the button is clicked, a list of trends influencing the pricing is proposed to adjust a number of prices, after which the values of a number of prices will be corrected. The method for adjusting price fluctuations is described in the following paragraphs of this section.
Planning methods

Note that the planning methods given here are designed to fill the rows quickly. Also use the usual editing - keyboard input, standard copy (Ctrl + C), insert (Ctrl + V), delete (Del), etc.
In the General case, procurement planning include:
- Planning the price. Tab "Procurement planning table".
- Setting the flow rate (normative) per unit of the product. The "Consumption (normative)" tab.
- Setting up the "procurement schedule". Tab "Purchase schedule" (if the type of costs is "material").
- Insurance stock planning. Material inventory accounting tab (if the cost type is "material").
Go to "procurement Planning", and call the editing form.
"Procurement plan and regulatory costs" (single click with the left mouse button, same F2):
In the form of "Procurement plan and regulatory costs" start to plan costs one way:
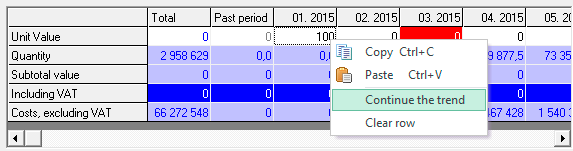
1 way. "Continue trend" function
Use the "continue the trend" if the price from the suppliers does not change as frequently, such as every six months. This is the easiest and fastest way fill a number of price trend.
- step. Enter the number in the (editable) cell where planning begins.
- step. Click the right mouse button (above the cell), and select "continue trend". As a result of the function, the row will be filled to the end.
The result of the "Continue trend" function:
- step. Select the next period when it is necessary to set a new price. Follow step 1,2 – starting any subsequent period...
2 way. Function "interpolation of the series by trend"
Use the function "interpolation of the series by trend", if you already have a filled series, and you need to interpolate the values of this series in the seasonal trend.
☛ Note that the function is called when a row already exists, when you click "Calculate".
- step. Enter the data using the "continue trend" function.
- step. If necessary, set the calculation start period.
- step. Click the "Calculate" button and select "interpolate the series by trend". As a result, the series will be filled to the end, taking into account seasonality factors.
 Steps 1-3 are performed separately - for planning either a price or an amount.
Steps 1-3 are performed separately - for planning either a price or an amount.
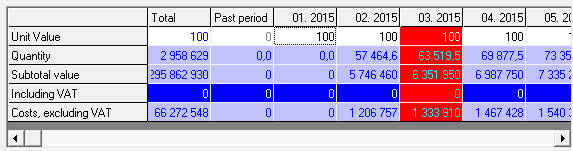
Example.
We set the price of "100" for some material, starting from the first month of the project,
as shown in the picture:
Let, target price will increase by 7% in 5-m and 10-m month. Install the appropriate values (in 5-m and 10-m month) in the seasonality trend of prices as shown in the figure below:
Click "Calculate" and execute point 2: "interpolation of the series by trend". As a result of executing, all the data of a number of prices, starting with 5-th and 10-th month, will increase by 7%.
Data of the calculation result are shown in table:
| Interpolation of a number of trend years |
Jan |
Feb |
March |
Apr |
May |
June |
July |
Aug |
Sen |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
| 1 year. Price changes in 5 and 10 month |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
107 |
107 |
107 |
107 |
107 |
114 |
114 |
114 |
| 2 year. Price changes in 5 and 10 month |
114 |
114 |
114 |
114 |
122 |
122 |
122 |
122 |
122 |
130 |
130 |
130 |
| 3 year. Price changes in 5 and 10 month |
130 |
130 |
130 |
130 |
139 |
139 |
139 |
139 |
139 |
148 |
148 |
148 |
 When using the "interpolation of the series by trend", new values (prices) are measured relative to the previous values, taking into account the seasonality coefficients.
When using the "interpolation of the series by trend", new values (prices) are measured relative to the previous values, taking into account the seasonality coefficients.
3 way. Plan the price "by annual values"
Use of sales planning "annual value" if you have defined the following parameters for prices: seasonality of price fluctuations and the prices at the beginning of the year.
☛ Note that the function is also called when you click the "Calculate" button, when all the seasonality values have already been edited.
- step. Enter the price for the beginning of the year, respectively, for 1,2 and 3 yeara.
- step. Adjust the seasonal price coefficients (from -100% to 100%).
- step. Click the "Calculate" button and select "by yearly values" .
Algorithm for calculating the price.
In the result of the calculation of "by annual values," the price for the beginning of each year is taken as the basis for calculating the price of the trend, according to the formula:
Price n = Price 1 × Coefficient n ,
Where:
Pricen - price in n period.
Price1 - price at the beginning of the year.
Coefficientn - (percentage of the seasonal factor)/100 in n period.
 Permissible fluctuations of seasonal prices can be from -100% to +100%. Seasonality of prices, in fact is deviation from the original series (in %).
Permissible fluctuations of seasonal prices can be from -100% to +100%. Seasonality of prices, in fact is deviation from the original series (in %).
Import data, edit
In addition to the above methods, the data can be imported, or simply enter values into the table.
Set the expense and schedule of purchases of materials

Tab "Schedule of purchases" are only available if the cost type "material".
- Consumption (standard)
To set the material consumption per unit of product, you need to select a product from the list and specify the consumption. Consumption can be specified for one or more products. To account for material consumption, you can set the number of decimal places from "0" to "4" in the "general settings".
From the main menu, you can call the function to export the report to Excel: "Material consumption per unit": "Reports → Export to Excel → Detailed reports → "Calculation of material consumption"":
 Scaling. In some cases it is not recommended to use decimal places, and in most cases it is enough to simply scale the units of measurement. For example, grams can be converted to milligrams (to reduce the scale), kilograms - to tons (zoom in), etc.
Scaling. In some cases it is not recommended to use decimal places, and in most cases it is enough to simply scale the units of measurement. For example, grams can be converted to milligrams (to reduce the scale), kilograms - to tons (zoom in), etc.
- Procurement schedule
Optionally, you can configure a schedule for procurement of materials and components, as shown in the figure. In the calculation of procurement takes into account real demand, including insurance of stocks of finished products and materials. In the example of the procurement for this material will be produced once a quarter:
Stock Planning
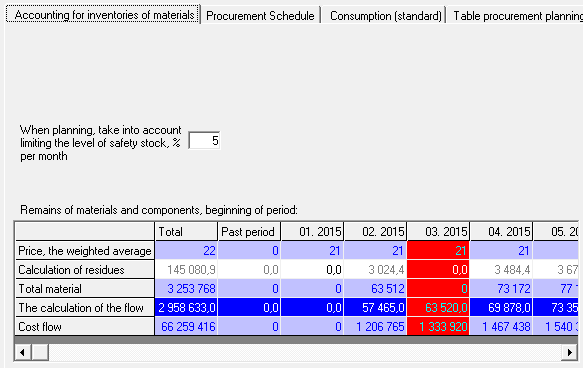
For stock planning, you need to go to the Inventory Accounting tab and specify the percentage in the "Stock level,% per month" field. After the completion of the final calculation, stocks will be displayed in the "Remains of materials and components at the beginning of the period" table.
 Only updated periods are available for stock editing.
Only updated periods are available for stock editing.
In the table "the remaining stock of materials and components at the beginning of the period" calculated string values:
- Price, weighted average (price without VAT)
- Calculation of residues.
- Calculation of costs.
- Cost of the expense.
Tab "inventory of materials":
 The values in the lines "costs" and "Cost of consumption" appear only after the final calculation of the edit form: ""Calculate" Button → full settlement", and also after the final calculation of the project: "Data → Calculate → "Procurement Plan"". Same F9.
The values in the lines "costs" and "Cost of consumption" appear only after the final calculation of the edit form: ""Calculate" Button → full settlement", and also after the final calculation of the project: "Data → Calculate → "Procurement Plan"". Same F9.
1. General algorithm for calculating stocks
First, it is necessary to calculate the "need" for production (or purchase of goods).
The need for production (or purchases of goods) is calculated by the formula:
Need[i] = Sales[i] + (Stocks at end of period[i+1] - Inventory beginning of period[i]) - Remains of the last period[0]
Where i is the period.
In the algorithm for calculating the needs of production (or purchases of goods), the following sequence is taken into account:
step 1. Calculation of sales plan;
step 2. Calculation of reserves at the beginning and end of periods;
step 3. the calculation of the needs of the production (or procurement of goods);
step 4. Calculation taking into account the residues of the previous period.
Stocks are calculated by a similar formula. But if in the first case we ensure the quality of the sales process
in the second case – of the procurement process:
Inventory[i] = Need[i] + (Stocks at end of period[i+1] - Inventory beginning of period[i]) - Remains of the last period[0]
Where i is the period.
The algorithm for calculating reserves takes into account the sequence:
step 1. Calculation of the plan of purchases (of specified needs and consumption per unit of product);
step 2. Calculation of reserves at the beginning and end of periods;
step 3. Calculation of reserves;
step 4. the Calculation of the account balances of the last period;
step 5. Calculation taking into account the schedule of the procurement.
2. Accuracy of calculations
To achieve the greatest accuracy, and to minimize relative errors, the maximum possible number of decimal places (32 characters) is used. The maximum relative error recorded in the test calculations was 1/10 000 000 (one ten millionth).
After the final calculation of the "costs" line, execute: ""Calculate" Button → Final calculation", the message is displayed:
3. Calculation of the weighted average price

Regardless of the chosen accounting method, only the weighted average price (without VAT) is considered in the table "Balance at the beginning of the period".
Inventories are not included in the "Profit and Loss Statement", but when calculating the cost, the value of inventories is taken into account, which will be realized in future periods. The total difference, recorded in the cost price and in the total cost of material inputs, in financial statements is defined as the difference between material costs and actual purchases - calculated by one of the accounting methods. For the carryover stock, which will be reflected in the balance line "Inventories", and to calculate the cost, a weighted average price or FIFO (depending on the chosen accounting method) should be found.
Note that the cost of inventories should reflect the full cost of material inputs - including transportation, storage, packaging costs and other costs that form the cost of material costs, if they are unconditionally included in the cost of costs. In any case, when planning the aggregate direct costs, it is necessary to take into account a number of the following factors:
- If costs are not included in the cost of material costs, they must be reflected in other lines.
- The expediency of creating an integrated material resource (from several materials and costs) should be justified.
- Total costs must contain the same VAT (or not have VAT).
- In case of irregular deliveries, purchases should be edited in accordance with the schedule.
 Select your Budget-Plan Express licenses and pay in your personal account - in rubles or other currency
Select your Budget-Plan Express licenses and pay in your personal account - in rubles or other currency
Help about the program "Budget-Plan Express", www.strategic-line.ru | Help contents
Share:

 When you click a button, a list of costs is offered - select the desired list item. In this case, the corresponding seasonal trend is loaded.
When you click a button, a list of costs is offered - select the desired list item. In this case, the corresponding seasonal trend is loaded.
 When the button is pressed, the current seasonality settings are saved, unsaved seasonal settings will be lost when their form is exited.
When the button is pressed, the current seasonality settings are saved, unsaved seasonal settings will be lost when their form is exited.
 When the button is clicked, a list of trends influencing the pricing is proposed to adjust a number of prices, after which the values of a number of prices will be corrected. The method for adjusting price fluctuations is described in the following paragraphs of this section.
When the button is clicked, a list of trends influencing the pricing is proposed to adjust a number of prices, after which the values of a number of prices will be corrected. The method for adjusting price fluctuations is described in the following paragraphs of this section.